When we discuss the human body and the many cells that make it function, we cannot forget to consider the impact and importance of the reproductive system. While many other aspects of the human body hold significance, this cannot be left out.
If you are interested in more about the cells in our bodies, visit the site to learn more.
Without considering the biological and cellular structure and functioning of our reproductive organs, we would lack knowledge on the factors that keep the human race as numerous and successful as it is.
One of the issues we face is infertility. Infertility is when our bodies cannot successfully produce offspring. It can occur for many different reasons and can be found in either partner in a sexual relationship. If a male and female person tries to procreate and cannot, at least one of the people shows signs of infertility.
In male infertility, recent studies connected mitochondria and their structure to the problem. Knowing this, we can use this knowledge to reverse and minimize the risk of male infertility.
Across the globe, approximately 9% of males and females are childless involuntarily due to biological factors. In a good 40-50% of these scenarios, the biological factors are within male infertility.
While many things can cause infertility in men, one of these causes is mutations in mitochondrial DNA.
Before we discuss how mitochondria can influence male infertility, let’s first explain what mitochondria are.
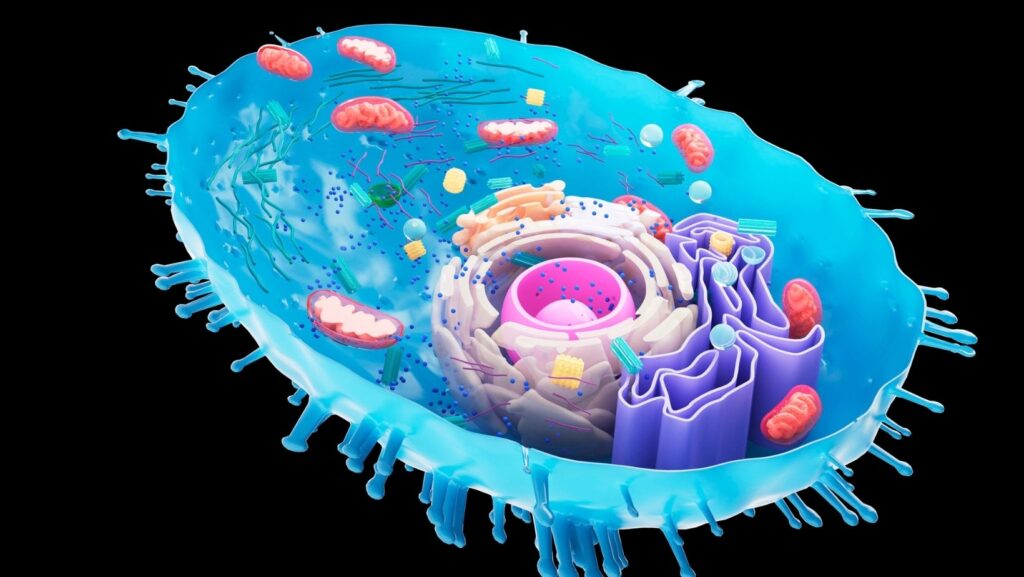
What Are Mitochondria?
Mitochondria are typically known as the powerhouse of the cell; they are what help us turn food into energy. That energy is then moved around our cells which can be put to use.
Yet, mitochondria do more than this; they are in nearly every cell in the human form and are pivotal to our survival. They can generate a vast majority of the energy inside our cells.
They are also involved in actions such as signaling from cell to cell.
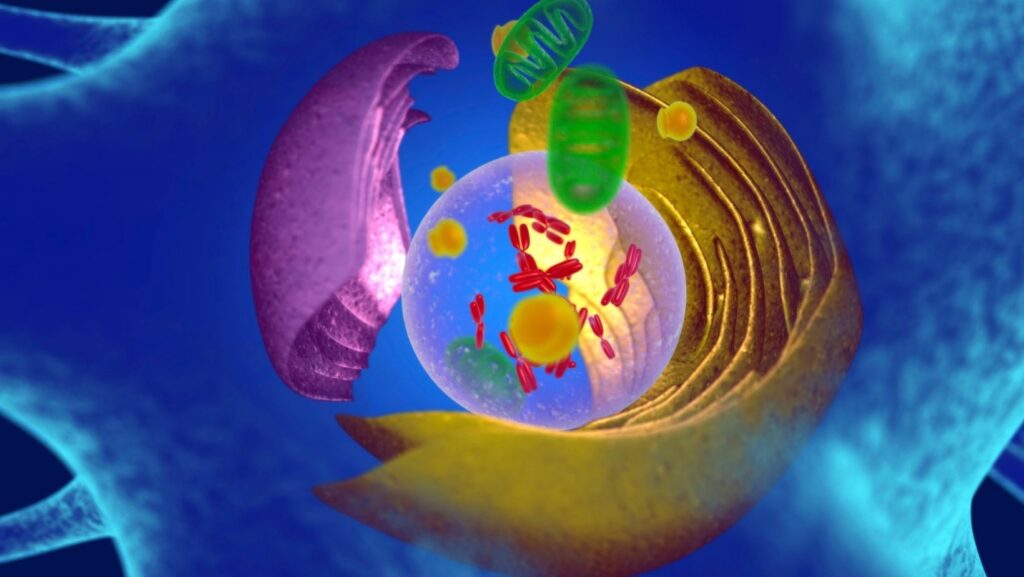
Mitochondria contain many parts, including strands of our DNA. They are tiny, and you cannot even see them beneath a microscope.
Unlike other mini-organs inside our cells, they have two membranes, one on the inside and another on the outside. They are split into different regions, many of which will carry out particular jobs and functions.
Every different cell will have a different type of mitochondria, mature cells will not have any, but your liver can have thousands. Cells that use up a great deal of energy will need a lot of mitochondria to be successful in their job.
An excellent example of this can be seen in the heart muscles. The cytoplasm in the heart muscle cells is made up of mitochondria (a whopping 40%!).
This means that mitochondria are in nearly every part of our bodies. This includes our sexual functions, such as sperm and eggs.
Mitochondria & Male Infertility
While infertility can happen for a vast number of reasons, a significant factor could be the mutations of DNA in mitochondria.
These mitochondria are mini-factories for energy in the cell that hold their own genome, the mtDNA.
Studies have shown that mice which have a large number of mutations in their mitochondrial DNA are usually infertile and will have little or no mobile sperm.
In sperm, there are many mitochondria present, but their jobs are not limited just to providing the sperm cells energy, as you may think.
These mitochondria have other jobs, too; this includes the production of steroid hormones in the testicles and the regulation of proliferation of the cells and cell death to maintain fertility.
However, mitochondria are absolutely crucial for the phosphorylation in sperm, as well as cholesterol efflux and the interaction between sperm and egg. However, they also play a large part in the processes, pathologically, in oxidative stresses.
Most male infertility cases we see today have an association with ROS-mediated damage to sperm. This can harm the structure and functional ability of the cells, including the membrane of the cell, DNA, and proteins inside the sperm.
This affects the mobility of the sperm and prevents it from being correctly able to penetrate the oocytes. It can also affect the efficient development of an embryo.
Studies in this area show that there are close links between low mitochondrial respiratory activity and a reduction in the mobility of sperm.
Having a lower mitochondrial membrane is also possible due to mutations that can cause low mobility in sperm.
It is entirely likely that the cause of low sperm motility is down to sub-par mitochondrial functionality.
It is known that proper mitochondrial functionality and a fully active membrane are absolutely necessary for not only sperm motility and production but all of the movements and requirements for healthy sperm and a healthy embryo upon insemination.
Should the mitochondrial function in sperm be defective, this will seriously impact the ability for energy production that is required for sperm to be properly mobile. This could therefore be the most direct cause of asthenozoospermia.
Not only this, but the mtDNA in sperm is also subject to potential mutations and oxidative damage, which would lead to issues with sperm function overall.
It would seem that a majority of males who have abnormal parameters in their semen usually have a much larger mtDNA copy and a reduction in the mtDNA’s integrity.
Simply put, sperm need healthy and well-grown mitochondria to function correctly. If the mitochondria are mutated or damaged, then this will affect the ability of the sperm or the body’s ability to produce sperm altogether.
What Is Co-Enzyme Q10 And Why Is It Important?
Co-enzyme Q10 (also known as CoQ10) is a natural nutrient found in your body. It is both made and stored in the mitochondria. As we said before, mitochondria are the mini-organs that produce energy, but without CoQ10, it is left unprotected against diseases and damages. If an individual’s sperm count is low from increasingly damaged sperm, the injuries could be due to a lack of CoQ10 to protect the mitochondria cells.
As you age, your mitochondria create less and less CoQ10, which is why fertility is often a problem after a certain age. Without the compound, the mitochondria cannot produce as much energy and are more susceptible to damage.
Food That Naturally Contains Co-Enzyme Q10
You can take CoQ10 supplements and add them to your morning vitamin regimen. As your body cannot store ingested CoQ10, you will not be at risk of overindulgence; however, it is a fat-soluble compound which means that your body will absorb it slowly.
To help get as much CoQ10 into your body, you can consume foods that produce the compound naturally. Adding them to your diet can make absorption more successful, which in turn makes your sperm’s mitochondria recovery more likely.
Food with high CoQ10 content are:
- Organs
- For example, liver and kidneys.
- Fatty Fish
- For example, sardines, trout, and mackerel.
- Meat in general
- For example, classic meats such as chicken and pork.
- Oils
- Specifically canola and soybean oils.
- Vegetables
- Specifically broccoli, cauliflower, and spinach.
- Fruit:
- Specifically strawberries and oranges.
- Nuts:
- Specifically pistachios.
- Legumes:
- Specifically lentils and soybeans.
Adding more of these foods into your diet will boost the amount of CoQ10 in your system. For the biggest benefit, we suggest including as many organ meats as possible.
Recipes That Are Beneficial Against Mitochondria Related Infertility
Putting ingredients in front of you and saying they can boost your sperm’s success is one thing, but knowing what to do with those ingredients is another.
We will show you some recipes to help cook these beneficial foods so that you can add a couple to your diet.
Liver And Onions
This recipe takes 80 minutes to prepare and 25 minutes to cook, for a total of 105 minutes in the kitchen. It should serve four people when salads and mashed potatoes are added as sides.
Ingredients
- Beef Liver – 2 Pounds – Sliced
- Milk – 1 ½ Cups
- Butter – ¼ Cups – Divided
- Large Onions – 2 – Sliced into rings
- All-Purpose Flour – 1 Cups
- Salt
- Pepper
Method
When most people cook with liver, they end up with a bitter taste which they dislike. Our first step in this recipe removes that bitter taste to make your CoQ10 dose tasty.
Step 1:
First, you need to rinse your liver slices under cold water. Once cleaned, place them in a bowl. Then pour in the milk until the liver is covered. Leave them for up to an hour.
This method removes the bitter taste from the liver.
Step 2:
While the liver is soaking, cut the onions.
Step 3:
Using a large skillet, melt two tablespoons of the butter. Once melted, saute the onions until soft and brown. Then remove the onions, but keep the remaining butter in the pan.
Step 4:
Sprinkle a pinch of salt and pepper into the flour and mix. Lay the flour on a plate.
Step 5:
Remove the liver from the milk mixture and lay it onto the flour. Coat both sides of the liver slices with the flour.
Step 6:
Place the flour-coated liver into the butter-coated skillet and cook until brown on the bottom. Turn the liver over and brown on the other side too. Add in the onions and reduce the heat.
The liver should have a barely pink color on the inside.
Smoked Trout And Pea Pasta
Trout is another ingredient that you might find hard to utilize, so we have created an easy recipe to help you find the best out of this CoQ10 heavy fish.
Ingredients
- Pasta (preferably fusilli) – 6 oz
- Frozen Peas – 4 oz
- Smoked trout – 5 oz
- Greek Yogurt – 3 Tablespoons
- Horseradish Sauce – 2 Teaspoons
- Salt
- Pepper
Method
This recipe should take 5 minutes to prepare and 15 minutes to cook. It serves two people.
Step 1:
Cook the pasta according to the package instructions. In the last 3 minutes of cooking, add the peas to the water.
Step 2:
As the pasta is cooking, flake the trout by putting a fork into the largest side and twisting it. The trout should easily fall apart.
Next, mix the yogurt, horseradish, salt, and pepper together.
Step 3:
Drain the pasta and peas, then mix in the trout and yogurt mixture. The heat of the pasta will warm the sauce.
Summary
CoQ10 is a crucial compound in our cells that protects our mitochondria. Mitochondria is in almost every cell in our body, including sperm cells. If we don’t have high CoQ10, our mitochondria will not be protected, causing it to fail at giving our cells energy.
Without the energy it needs, the sperm won’t have the mobility to reach the oocyte nor the power to correctly penetrate the oocyte.
To improve our CoQ10 count in our bodies, we can take supplements or eat CoQ10 rich foods like liver and trout.